Jan 5, 2026

IGF-1 DES (also called IGF-Des or des(1-3)IGF-1) represents one of the most sought-after research peptides in muscle growth and recovery applications, yet finding reliable sources requires navigating complex vendor landscapes with varying quality standards.
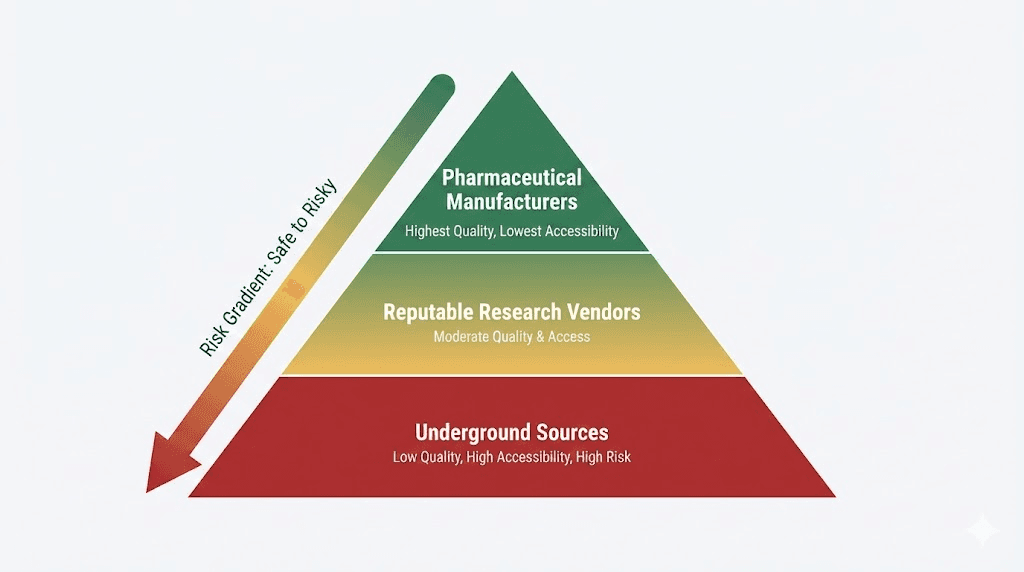
The research peptide market splits into distinct tiers creating sourcing challenges.
Pharmaceutical-grade manufacturers (Chinese API producers, legitimate chemical suppliers) provide highest purity (98-99%+) but typically sell only to established businesses with proper documentation and minimum order quantities (10-100 grams, $5,000-$50,000+ orders).
Research chemical vendors (operating in regulatory gray areas) offer smaller quantities (1-10mg) to individuals at $50-$300 per mg depending on purity and vendor reputation, accessibility easier but quality highly variable. Underground labs and black market sources provide cheapest options ($20-$100 per mg) with essentially zero quality assurance, high contamination and underdosing risks.
SeekPeptides helps navigate these tiers identifying legitimate sources while avoiding scams and dangerous products.
Here we cover verified vendor categories and evaluation criteria, detailed Certificate of Analysis assessment methods, independent testing procedures and laboratory options, legal and regulatory considerations by jurisdiction, comparing IGF-Des to related peptides (IGF-1 LR3, standard IGF-1, growth hormone peptides), pricing analysis and value assessment, quality verification protocols preventing contamination and underdosing, safety considerations for research use, and future sourcing landscape as regulations evolve. SeekPeptides serves as trusted resource for peptide vendor information and quality verification strategies.
Let's examine vendor categories and evaluation frameworks for identifying reliable IGF-Des sources.
Understanding IGF-Des vendor landscape
Different supplier types serve distinct markets with varying quality, accessibility, and legitimacy levels.
Pharmaceutical API manufacturers
Chinese chemical synthesis companies: Major players in global peptide production include companies like GenScript, GL Biochem, ChinaPeptides, and numerous smaller manufacturers. Produce pharmaceutical-grade IGF-Des as active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) for drug development and research. Purity typically 98-99%+ verified through comprehensive analytical testing (HPLC, mass spec, amino acid analysis). Minimum order quantities prohibitive for individuals (10-100g, $5,000-$50,000+ depending on synthesis difficulty and quantity).
Legitimate wholesale access: Requires business documentation (tax ID, research institution affiliation, purchase orders). Intended customers include pharmaceutical companies, contract research organizations, university laboratories. Individual researchers without institutional backing cannot typically access directly. However, some research chemical vendors source from these manufacturers creating indirect access path.
Quality assurance: Pharmaceutical manufacturers maintain rigorous quality control for regulatory compliance and reputation protection. Batch testing standard with comprehensive documentation. Product purity reliable when sourced directly though chain of custody matters, peptides potentially degrading or becoming contaminated during distribution if not handled properly. Understanding peptide stability critical for maintaining quality through distribution.
Research chemical vendors (gray market)
Established vendors with reputation: Companies like Peptide Sciences, Limitless Life, Swiss Chems, and others operating 3+ years with community track records. Sell to individuals without institutional requirements. Provide Certificates of Analysis (varying legitimacy), accept credit card or cryptocurrency payment. Pricing $75-$300 per mg IGF-Des depending on vendor and quantity. Accessibility higher than pharmaceutical sources though quality varies.
Verification importance: Not all research chemical vendors equal. Some source from legitimate manufacturers maintaining quality. Others use questionable suppliers or manufacture in-house without proper quality control. Vendor verification through community testing, COA analysis, and independent lab testing essential before trusting any vendor.
Underground and black market sources
Bodybuilding forums and encrypted marketplaces: Private vendors operating through Telegram, Discord, bodybuilding forums, or darknet markets. Lowest prices ($20-$100 per mg) but highest risk. Zero quality assurance, frequent underdosing (product containing 30-50% stated amount or less), contamination risks (heavy metals, bacteria, wrong compounds), exit scam potential (vendor disappears after payments).
Why people use despite risks: Price point attractive for those experimenting or on tight budgets. Accessibility through anonymous cryptocurrency transactions. However, false economy as underdosed or fake product wastes money regardless of low nominal price. Health risks from contamination potentially severe.
Risk assessment: Only consider if desperate and cannot access better sources, always verify through independent testing before use, never trust vendor claims or reviews (easily faked), prepare for product loss if vendor disappears or product fake. Understanding research chemical risks prevents dangerous situations.
Compounding pharmacies (limited availability)
Prescription-based access: Some compounding pharmacies prepare peptide formulations with physician prescription. IGF-Des not FDA-approved medication limiting prescription justification. Most physicians unwilling prescribing for muscle growth applications. Possible for legitimate medical research under physician supervision though rare.
Quality advantages: Licensed pharmacy oversight ensures sterility, purity verification, proper formulation. Eliminates many risks associated with research chemical vendors. However, extremely limited availability for IGF-Des specifically.
Vendor Type | Purity Range | Price/mg IGF-Des | Minimum Order | Accessibility | Quality Assurance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Pharmaceutical API | 98-99%+ | $50-$150 (bulk) | 10-100g ($5k-$50k) | Business/Institution only | Excellent |
Research Chemical (reputable) | 95-98% | $75-$300 | 1-10mg | Individual friendly | Moderate (verify) |
Research Chemical (unknown) | 60-95% | $50-$150 | 1-10mg | Easy | Poor (test required) |
Underground/Black Market | 30-90% | $20-$100 | 1-5mg | Very Easy | None (high risk) |
Compounding Pharmacy | 98-99% | $300-$500+ | Per prescription | Prescription required | Excellent |
Certificate of Analysis evaluation methods
COAs prove nothing without critical assessment of authenticity and relevance.
Identifying legitimate vs fake COAs
Batch number matching: Legitimate COA includes batch or lot number matching product label. Verify batch number on your product matches COA batch number. Generic COAs without batch numbers or mismatched numbers indicate fake documentation. Request batch-specific COA for your order, not generic analysis from different batch potentially months or years old.
Independent laboratory attribution: Real COAs specify testing laboratory name, address, contact information. Generic "in-house testing" or "quality control department" without specific lab details suggests fake. Verify laboratory existence through internet search, phone number verification. Some scammers create fake lab names sounding legitimate.
Comprehensive testing panels: Pharmaceutical-grade COAs include HPLC purity (showing peptide percentage and impurity profile), mass spectrometry (confirming molecular weight matching IGF-Des), amino acid analysis (verifying sequence), bacterial endotoxin testing, heavy metal screening. Research vendor COAs might only show HPLC purity, acceptable but less comprehensive. COAs claiming "99.9% pure" without any analytical data highly suspect.
Date relevance: Testing date should be recent relative to product manufacturing and sale. COA from 2-3 years ago for product sold today suggests either very old inventory or fake COA. Peptides degrade over time, old testing results don't represent current product quality.
Professional formatting: Legitimate laboratory COAs use professional templates with clear organization, proper scientific terminology, appropriate units (mg, %, ppm). Homemade-looking documents with spelling errors, unprofessional formatting, or inconsistent data presentation raise red flags. However, sophisticated scammers can fake professional appearance, so format alone insufficient for verification.
HPLC interpretation for peptide purity
Peak analysis: HPLC chromatogram shows peaks representing different compounds in sample. Main peak should represent IGF-Des with area under curve correlating to percentage purity. Smaller peaks represent impurities (truncated sequences, synthesis byproducts, degradation products). Purity calculated as (IGF-Des peak area / total peak area) × 100.
Purity thresholds: Pharmaceutical-grade IGF-Des should show 98-99%+ purity. Research-grade 95-98% acceptable. Below 95% suggests poor synthesis or degradation. Below 90% likely underdosed or heavily contaminated. Purity directly impacts dosing, 90% pure product requires 10% higher dose achieving equivalent effect versus 99% pure.
Impurity profiles: Pattern of impurity peaks can indicate synthesis quality. Many small peaks suggest incomplete purification. Large impurity peaks might indicate specific synthesis problems or degradation. Completely clean chromatogram with only IGF-Des peak and no impurities seems suspicious (synthesis always produces some impurities, completely pure suspicious for being too good to be true or faked data).
Method validation: COA should specify HPLC method (column type, mobile phase, flow rate, detection wavelength). Standard methods exist for peptide analysis, unusual or vague method descriptions raise concerns. Properly validated methods ensure accurate purity determination. Learn about analytical methods for comprehensive understanding.
Mass spectrometry confirmation
Molecular weight verification: Mass spectrometry measures exact molecular weight of compounds in sample. IGF-Des has theoretical molecular weight ~7,100-7,200 Da (depending on exact sequence and modifications). Mass spec should show peak at expected molecular weight confirming identity. Wrong molecular weight indicates different peptide or contamination.
Fragmentation patterns: Advanced mass spec (MS/MS or tandem mass spec) fragments peptide and analyzes pieces. Fragment pattern unique to specific peptide sequence like fingerprint. Confirms not just molecular weight but actual sequence. More definitive than simple mass spec though more expensive and not always included in standard COAs.
Contaminant detection: Mass spec can identify unexpected peaks representing contaminants. Might reveal presence of related peptides (IGF-1 LR3, standard IGF-1), completely different compounds, or degradation products. Comprehensive mass spec analysis valuable for quality assessment beyond just purity percentage.
Limitations: Mass spec highly accurate for molecular weight but doesn't quantify purity as precisely as HPLC. Combination HPLC (for purity quantification) plus mass spec (for identity confirmation) provides most comprehensive analysis. Vendors providing both inspire higher confidence than those offering only one or the other.
Verifying laboratory credentials
Laboratory accreditation: Legitimate analytical labs hold accreditations from organizations like ISO 17025 (international standard for testing laboratories). Accreditation verifies laboratory follows proper quality management systems, maintains equipment calibration, employs trained personnel. Check laboratory website for accreditation certificates and scope.
Contact verification: Call laboratory using number from their website (not number on COA which could be fake). Verify they performed testing for specific vendor. Some vendors use real laboratory names on fake COAs. Laboratory can confirm whether they tested product and if COA matches their records. Most reputable labs willing to verify upon request.
Previous customer experiences: Search for laboratory name in peptide community forums (Reddit, Longecity, others). Other users' experiences with same laboratory provide insights into reliability. Consistent positive reviews versus any scam warnings or quality concerns. SeekPeptides aggregates laboratory reviews from community.
Red flags indicating fake or misleading COAs
Multiple vendors using identical COAs: If several different vendors all provide identical COA (same batch numbers, dates, results), clearly fake. Each vendor's products should have unique testing documentation.
Impossibly perfect results: All parameters showing exactly 99.9% or 100% purity with zero impurities detected seems too perfect. Real analytical results show some variability and typically detect trace impurities even in high-quality products.
Inconsistent data: HPLC purity says 98% but mass spec says 95% (methods should produce similar results), conflicting information within single COA suggests fabrication.
Vendor refuses batch-specific COA: If vendor only provides generic COA claiming it represents all batches without offering batch-specific testing, indicates lack of actual quality control. Legitimate operations test each batch or at minimum provide batch-specific documentation.
No response to verification requests: Requesting laboratory contact information or batch number verification met with evasion, excuses, or no response suggests vendor hiding something. Legitimate vendors with real COAs happy to provide verification information.
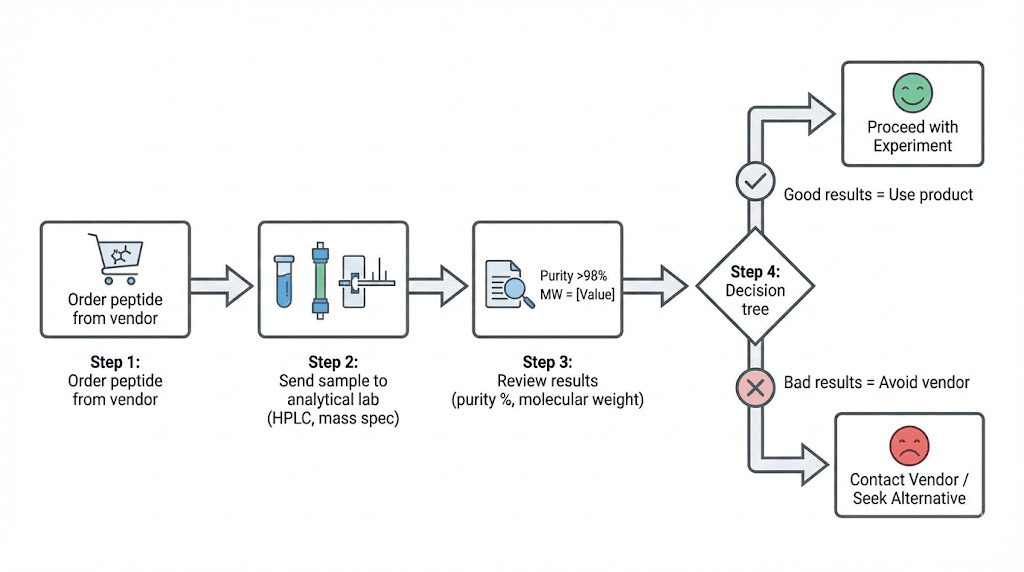
Independent testing procedures and laboratory options
Only reliable verification comes from testing you arrange independently of vendor.
Selecting analytical laboratories
Colmaric Analyticals: Specialized peptide testing service popular in research peptide community. HPLC purity testing $75-$100, mass spec $100-$150, combination packages available. Turnaround 7-14 days typically. Online ordering, mail samples. Focus on peptides means expertise in relevant analytical methods. Website provides detailed testing information and sample submission instructions.
Janoshik Analytical: European-based testing service with strong reputation in performance enhancement community. Similar pricing to Colmaric ($75-$125 for HPLC, $100-$175 for mass spec). Faster turnaround (5-10 days) sometimes available. Accepts international samples. Known for thorough testing and professional communication.
Energy Control: Harm reduction organization providing substance testing. Not peptide-specialized but capable of basic purity and identity testing. Lower cost ($40-$80) but less peptide expertise. Primarily serves drug checking purposes but applicable to peptides.
University analytical facilities: Some universities offer testing services to public for fee. Contact chemistry departments inquiring about analytical services. Pricing variable ($100-$300) depending on institution and testing requested. Availability limited, academic schedules may affect turnaround times. However, high credibility using same equipment as pharmaceutical research.
Considerations for selection: Cost versus comprehensiveness balance (basic HPLC sufficient for purity check, mass spec adds identity confirmation), turnaround time (faster results cost more), laboratory reputation in peptide community (established track record provides confidence), sample submission process (some require specific packaging, shipping methods). SeekPeptides provides laboratory comparison guides helping selection.
Sample preparation and submission
Sample size requirements: Laboratories typically need 1-5mg powder for testing. From 5mg vial, submit 1mg leaving remainder for actual use. Carefully weigh using milligram scale (required for peptide reconstitution anyway). Submit slightly more than minimum ensuring adequate sample for analysis including any necessary retesting.
Packaging requirements: Seal sample in small plastic bag or vial preventing spillage. Laboratory specific packaging instructions on website, follow precisely. Include clear labeling with your order number or identifier. Some laboratories provide pre-paid shipping labels, others require standard mail or specific carriers. Room temperature shipping typically acceptable for lyophilized powder though some prefer cold packs for longer transit times.
Anonymity considerations: Most testing services allow anonymous or pseudonymous submission. Use non-identifying information on packages if concerned about privacy. Payment via cryptocurrency maintains anonymity versus credit cards linking to real identity. However, legitimate testing use should not require hiding, anonymity more relevant for borderline legal situations.
Documentation: Photograph sample before submission (proving you sent actual product not random powder). Save submission confirmation emails and tracking numbers. Documentation helpful if disputes arise or results need verification.
Interpreting test results
Purity confirmation: Results showing 95-99% purity indicate good quality product worth using. 90-95% acceptable though may require slightly higher dosing compensating for lower purity. 85-90% marginal, consider whether vendor worth continuing based on price and alternatives. Below 85% likely not worth using, vendor unreliable.
Identity verification: Mass spec confirming IGF-Des molecular weight critical. Some vendors substitute cheaper peptides (standard IGF-1, completely unrelated compounds) hoping customers won't test. Wrong molecular weight means wrong product regardless of purity percentage.
Contaminant assessment: Heavy metals below detection limits ideal. Bacterial endotoxins tested in pharmaceutical contexts less relevant for peptides not intended for injection though good data point. Unexpected compound peaks raise concerns requiring investigation.
Decision making: Results showing good purity (95%+) and correct identity (IGF-Des molecular weight confirmed) indicate vendor reliable for that batch. Retest future orders periodically ensuring continued quality.
Poor results (low purity, wrong identity, contaminants) mean avoid vendor, report to community, request refund (though success unlikely with research vendors).
Community testing initiatives
Group buys for testing: Multiple individuals purchasing from same vendor pool funds ($10-$20 each) sending sample for testing. Results shared benefiting everyone. Reduces individual cost while maintaining verification. Coordinated through Reddit, Discord, or specialized forums.
Shared databases: Communities like Reddit r/Peptides, Longecity forums, or specialized Discord servers maintain vendor testing result databases. Members contribute test results creating collective knowledge. Search database before purchasing identifying tested vendors and batches. Contribute your results helping others.
Verification circles: Trusted community members with established credibility test vendors and share findings. Follow respected testers (people with histories of accurate reporting and no vendor affiliations). However, remain skeptical even of community results, some vendors fake community reviews or manipulate testing circles.
Cost sharing models: Some community initiatives formalize testing cost sharing. Monthly or quarterly vendor sampling programs where members contribute set amount ($25-$50) and designated testers purchase and test popular vendors. Results published benefiting entire community. SeekPeptides facilitates community testing programs connecting users for collaborative verification.
Legal and regulatory considerations by jurisdiction
IGF-Des legal status varies dramatically across countries and regions.
United States regulatory framework
FDA status: IGF-Des not approved for any medical use. Classified as unapproved drug if marketed for human consumption. Legal for research purposes when properly labeled "not for human consumption" and sold to qualified researchers. However, enforcement focuses on distribution and marketing rather than personal possession for research.
DEA scheduling: Not controlled substance under federal drug scheduling. Possession not criminal offense like scheduled drugs. However, marketing for performance enhancement potentially violates anti-doping regulations (WADA prohibited list) and FDA food/drug regulations.
Research exemption: Chemical suppliers can sell IGF-Des for legitimate research to qualified institutions. "Research purposes only" labeling provides legal cover though vendors rarely verify actual research use. Effectively creates gray market accessible to individuals despite legal ambiguity.
State variations: Some states (California, Oregon, others) have specific laws around performance-enhancing substances. Possession of peptides without prescription potentially illegal in these jurisdictions though enforcement rare. Check state-specific regulations if concerned.
Customs and importation: Importing IGF-Des from international sources risks customs seizure. Small quantities (personal use amounts, single vial) sometimes pass but seizure possible. Large quantities face higher interdiction rates and potential legal consequences. Domestic vendors eliminate importation risks though may charge premium.
Practical enforcement: FDA and DEA primarily target large-scale distribution and manufacturing operations, not individual end-users for personal use. Small possession for research purposes extremely low enforcement priority. However, no absolute legal protection, individuals proceeding accept some legal ambiguity. Understanding peptide legality helps informed decisions.
European Union regulatory status
General framework: Individual member states regulate medicines and research chemicals differently. Some countries (Netherlands, Czech Republic) relatively permissive. Others (Norway, Sweden, Germany) strictly enforce medication regulations. No harmonized EU-wide policy for research peptides creates complex patchwork.
Research chemical classification: When labeled "not for human consumption" and sold for research, IGF-Des occupies legal gray area similar to US. Legitimate research chemical vendors operate openly in permissive countries shipping throughout EU single market.
Novel Food Regulation: EU Novel Food Regulation potentially affects peptides marketed as supplements. IGF-Des not approved novel food, cannot be legally sold as dietary supplement or food product. Research chemical labeling avoids this restriction.
Country-specific considerations: Germany strictly enforces medication laws, customs actively screens peptide shipments. UK (post-Brexit) maintains medication control though research chemical market active. Netherlands, Portugal, Spain more permissive with established research chemical vendors. France variable enforcement. Check specific country regulations if ordering.
Other major jurisdictions
Canada: Health Canada regulates IGF-Des as prescription drug if intended for human use. Research purposes potentially legal though ambiguous. Customs strict on importation, high seizure rates. Domestic Canadian vendors limited, most individuals source from US or international suppliers accepting seizure risk.
Australia: Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) strictly controls peptides. IGF-Des Schedule 4 (prescription only). Importation highly restricted, customs aggressive screening. Few legitimate domestic sources. Most Australians face significant sourcing challenges, international orders frequently seized.
United Kingdom: Post-Brexit UK maintains prescription-only status for IGF-Des. Possession without prescription technically illegal though enforcement targets suppliers not users. Research chemical market active despite legal restrictions. Customs screening moderate, some international shipments successfully delivered.
Asia (variable): China manufactures most global IGF-Des but domestic regulations complex. India, Thailand more permissive with available domestic sources. Japan, South Korea strict control. Hong Kong, Singapore variable.
Shipping and customs considerations
Domestic shipping: Avoid customs entirely ordering from vendors in your country. Higher prices potentially but eliminates seizure risk and faster delivery. Domestic law enforcement rarely intercepts domestic shipments unless extremely large quantities suggesting distribution.
International shipping challenges: Customs screens packages from certain countries (China, India) more aggressively than others. Peptide shipments potentially flagged through X-ray appearance, labeling, or country of origin. Seizure results in notice letter explaining violation, product confiscated. No criminal prosecution for small personal amounts typically though possible for large quantities.
Stealth shipping: Some international vendors use creative packaging hiding products. Effectiveness variable and declining as customs adapt. Moral hazard where successful stealth shipment creates false confidence in repeated orders until inevitable seizure. Not guaranteed success method.
Success rates: Vary dramatically by destination country, source country, package size, vendor packaging practices. Estimates range 50-90% successful delivery depending on variables. Some individuals accept 30-50% seizure rates budgeting accordingly. Others refuse international sources due to unreliability.
Legal consequences: Most small seizures result only in lost product and warning letter. Large quantities or repeated seizures may trigger investigation though rare. Commercial quantities (hundreds of vials) face serious legal risk including prosecution. Personal amounts (1-10 vials) generally low consequence. Consult importation guides for jurisdiction-specific information.
Comparing IGF-Des to related peptides
Understanding alternatives helps determining whether IGF-Des specifically needed or substitutes acceptable.
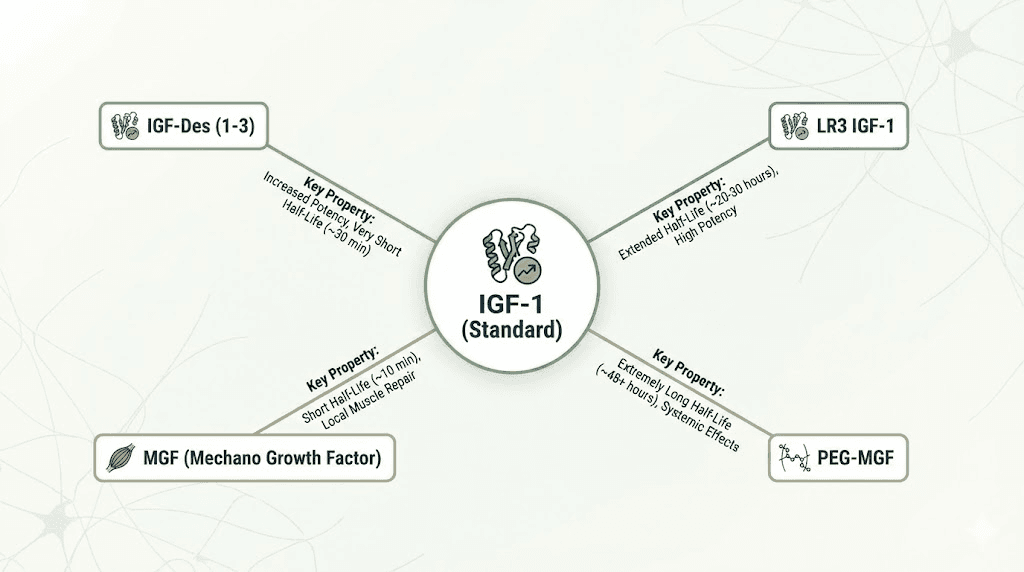
IGF-1 LR3 vs IGF-Des
Structural differences: IGF-1 LR3 modified at position 3 (glutamic acid substitution) and extended 13 amino acids creating longer 83-amino acid peptide. IGF-Des truncated version missing first 3 amino acids creating shorter 67-amino acid peptide. Different modifications produce distinct properties.
Half-life comparison: LR3 half-life approximately 20-30 hours allowing once-daily dosing. IGF-Des half-life only 20-30 minutes requiring multiple daily injections. LR3 convenience superior though IGF-Des advocates prefer shorter half-life for more precise timing control and rapid clearance.
Potency differences: IGF-Des roughly 10x more potent than LR3 for local tissue effects due to reduced binding protein affinity. Creates higher free (active) peptide levels locally. However, LR3's longer half-life and systemic distribution compensate creating similar overall effects at appropriate doses.
Practical usage: LR3 easier protocol (once daily injection, longer stability reconstituted) making it more user-friendly. IGF-Des requires more frequent injection, careful timing around workouts, shorter shelf life. However, some users prefer Des for site-specific effects (injecting directly into target muscles). Cost generally similar per effective dose. Learn about IGF variant comparison for detailed analysis.
Availability: LR3 generally easier to source with more vendors offering and less synthesis difficulty. IGF-Des fewer reliable vendors due to synthesis complexity. Some vendors offering both allowing experimentation determining personal preference.
Growth hormone peptides vs IGF peptides
Indirect vs direct IGF elevation: Growth hormone peptides like Ipamorelin, CJC-1295, and MK-677 stimulate natural growth hormone production. Growth hormone then stimulates liver IGF-1 production creating indirect pathway. Direct IGF-Des administration bypasses this providing immediate IGF effects without growth hormone elevation.
Systemic vs local effects: Growth hormone peptides create body-wide effects (elevated GH and IGF-1 throughout system). IGF-Des especially with local injection creates concentrated effects in target tissue. Different applications depending on goals, body composition goals might prefer systemic GH peptides while localized muscle enhancement favors IGF-Des.
Regulatory differences: Growth hormone secretagogues (Ipamorelin, MK-677) face similar research chemical status as IGF peptides. CJC-1295 sometimes pharmaceutical-grade available. Regulatory landscape similar though specific country/jurisdiction variations exist.
Cost comparison: Monthly protocols vary widely. Growth hormone peptide stack (Ipamorelin + CJC-1295) $100-$300 monthly. IGF-Des $150-$500 monthly depending on dosing frequency and vendor. LR3 $100-$400 monthly. Costs similar ranges though individual vendor pricing varies substantially.
Safety profiles: All research peptides carry similar experimental risks (unknown long-term effects, individual response variability, quality/purity concerns). Growth hormone peptides potentially safer long-term as working through natural pathways versus direct exogenous IGF. However, insufficient human data for definitive safety comparisons. Review GH vs IGF approaches for comprehensive analysis.
Standard recombinant IGF-1
Full-length peptide: Standard IGF-1 (somatomedin C) complete 70-amino acid peptide produced by liver in response to growth hormone. Recombinant versions produced for research use. Less modified than LR3 or Des making it closest to endogenous hormone.
Binding protein interactions: Standard IGF-1 binds IGFBPs (insulin-like growth factor binding proteins) strongly limiting free active peptide. Most circulating IGF-1 bound and inactive at any time. IGF-Des and LR3 designed to reduce IGFBP binding increasing free active fraction.
Clinical context: FDA-approved IGF-1 (Mecasermin/Increlex) exists for treating IGF-1 deficiency in children. Pharmaceutical product with established safety profile for medical use. However, prescription-only and expensive ($5,000-$10,000+ per month). Research chemical recombinant IGF-1 available but less common than LR3 or Des variants.
Research use rationale: Standard IGF-1 less popular for muscle enhancement due to strong IGFBP binding reducing potency. Modified versions (LR3, Des) preferred for research applications. Standard form primarily used in pharmaceutical contexts or specific research protocols requiring unmodified peptide.
Mechanical growth factor (MGF) peptides
Splice variant: MGF (mechano growth factor) splice variant of IGF-1 gene produced in response to mechanical stress (exercise). Contains unique C-terminal sequence creating different biological properties. Theoretically promotes satellite cell activation and muscle repair distinct from standard IGF-1 effects.
PEG-MGF modification: Pegylated MGF with extended half-life similar to IGF-1 LR3 modification concept. Research chemical vendors offer PEG-MGF claiming superior muscle growth versus other IGF variants. However, limited research on MGF effectiveness and optimal use.
Evidence limitations: MGF research mostly preclinical (animal and cell culture studies). Human clinical data minimal compared to standard IGF-1 research. Uncertain whether recombinant MGF produces claimed benefits or if endogenous MGF research translates to exogenous administration effects.
Practical considerations: Availability limited versus IGF-Des or LR3. Higher synthesis cost reduces vendor offerings. Less community experience and dosing protocols established. More experimental choice requiring higher risk tolerance. SeekPeptides covers MGF peptides for those interested in less common variants.
Peptide | Half-Life | Potency vs Standard IGF-1 | Typical Dosing | Primary Use | Availability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
IGF-1 DES | 20-30 min | 10x (local) | 50-150mcg multi-daily | Site-specific growth | Moderate |
IGF-1 LR3 | 20-30 hours | 2-3x | 20-80mcg daily | Systemic growth | Good |
Standard IGF-1 | 12-15 hours | 1x (baseline) | Clinical dosing | Medical use | Limited (Rx) |
PEG-MGF | 24-48 hours | Unknown | 100-200mcg post-workout | Recovery/repair | Limited |
GH Peptides (Ipa+CJC) | Variable | Indirect (via GH) | Protocol dependent | Systemic GH/IGF boost | Good |
Pricing analysis and value assessment
Understanding market pricing prevents overpaying while recognizing when low prices indicate problems.
Market price ranges by vendor tier
Pharmaceutical bulk suppliers: When accessible (business accounts, large orders), bulk pricing $5-$15 per mg for pharmaceutical-grade 98-99% purity. However, minimum orders 1000-10,000mg ($5,000-$150,000) making this completely impractical for individual users. Included only for reference showing actual production costs, retail markup significant.
Established research vendors: Reputable vendors with testing documentation charge $100-$300 per mg depending on quantity discounts. 1mg vial $100-$150. 5mg vial $400-$700. 10mg vial $800-$1,200. Bulk discounts 10-20% for larger quantities. Pricing reflects quality assurance costs, small-scale distribution, regulatory/legal risks.
Newer/unknown vendors: Less established sources charge $50-$150 per mg positioning as discount alternative. However, quality highly uncertain. Apparent savings evaporate if product significantly underdosed or contaminated. Only consider if willing to independently test before use.
Underground market: Black market prices $20-$100 per mg varying widely based on source reputation, current supply/demand, negotiation. Lowest nominal prices but highest risk of fake/underdosed product. Real cost much higher when factoring product loss risk and health dangers from contamination.
Calculating cost per protocol
Typical IGF-Des protocols: Research indicates 50-100mcg (0.05-0.1mg) post-workout or split doses daily. Monthly usage 4-12mg depending on frequency and dose. At $150/mg, monthly cost $600-$1,800. More affordable $75/mg vendors reduce to $300-$900 monthly. Protocol costs substantial, budgeting essential.
Comparison to alternatives: IGF-1 LR3 protocols using 20-40mcg daily consume 0.6-1.2mg monthly, $60-$360 at similar per-mg pricing. Growth hormone peptide protocols (Ipamorelin + CJC-1295) cost $100-$300 monthly. Alternatives sometimes more cost-effective achieving similar goals.
Duration requirements: Most protocols run 4-8 weeks with 4-week breaks preventing receptor downregulation. Multiple cycles yearly for sustained benefits. Annual costs $2,400-$7,200+ for serious IGF-Des use. Long-term financial sustainability critical consideration versus short-term experimentation.
Value assessment factors
Purity premium: 98% pure IGF-Des at $150/mg versus 85% pure at $75/mg, true cost per pure peptide similar ($150 per mg of 98% pure = $153 per mg pure peptide, $75 per mg of 85% pure = $88 per mg pure peptide). However, impurities bring unknown contamination risks beyond just reduced dosing. Higher purity worth premium for safety not just cost-per-pure-peptide calculations.
Testing costs: Adding independent testing ($75-$150) to first vendor order increases effective cost. However, one test verifies entire batch (multiple vials from same batch don't need individual testing). Test cost amortized across multiple vials. Testing $150 for verification plus $300 for 3 vials ($150 per vial) = $600 total, $200 per verified vial. Subsequent same-batch orders avoid testing costs.
Reliability value: Established vendor charging premium but delivering consistently good product versus cheap vendor with variable quality. Premium vendor reduces time/stress researching alternatives, wasted money on bad batches, potential health issues from contamination. Reliability premium worthwhile for many users. SeekPeptides helps vendor value assessment weighing cost versus quality.
Identifying pricing red flags
Too cheap to be real: IGF-Des at $20-$30/mg when market rates $100-$300/mg indicates either extremely poor quality, complete fake, or scam operation. Real synthesis and quality control cost money. Legitimate vendors cannot sustainably sell far below market rates. Extreme discounts suggest problems.
Unrealistic bulk discounts: Vendor offering 5mg for $50 ($10/mg) when single mg costs $150 raises questions. Bulk discounts exist (10-30% typical for 10x quantities) but shouldn't drastically undercut single vial pricing. Suspicious pricing structures suggest bait-and-switch or selective scamming.
Constant "sales" and urgency: Perpetual 50-70% off sales with countdown timers create false urgency. Legitimate research chemical market doesn't require aggressive sales tactics. Constant discounting suggests either inflated regular prices or pressure tactics compensating for poor reputation.
Price too good considering claimed quality: Vendor claiming pharmaceutical-grade 99% purity but charging budget prices ($50/mg) doesn't align. Quality testing, proper storage, small-batch distribution cost money. Price and quality claims should correlate logically.
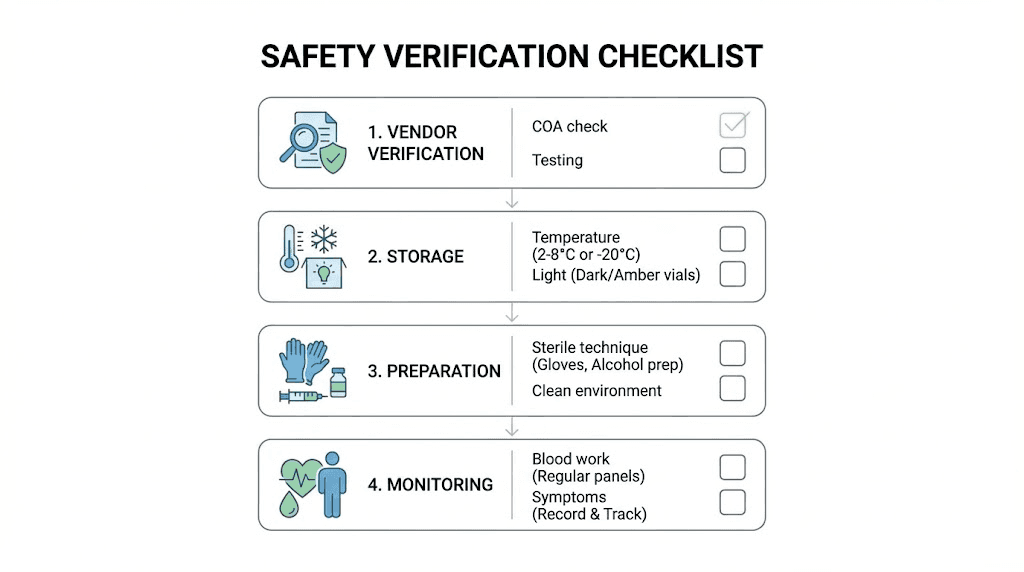
Quality verification protocols
Beyond initial testing, ongoing verification ensures continued reliability.
Batch testing strategy
Initial vendor evaluation: Test first order from new vendor establishing baseline quality. If results good (95%+ purity, correct identity), vendor passes initial screening. If results poor, avoid vendor entirely regardless of excuses or promises.
Periodic re-testing: Even reliable vendors can change suppliers or degrade quality. Retest periodically (every 6-12 months or every 5-10 vials) ensuring continued quality. Some vendors maintain quality initially then decline after establishing customer base.
Batch number tracking: Record batch numbers from all orders. If quality issues arise, identify which batches affected. Batch-specific problems may not reflect all vendor inventory. However, multiple bad batches from same vendor indicates systemic quality issues.
New batch verification: When batch numbers change significantly or long gaps between orders, consider retesting. New batches represent different synthesis runs potentially different quality. Conservative approach tests each new batch though expensive for frequent buyers.
Visual inspection (limited value)
Appearance assessment: Lyophilized IGF-Des should be white to off-white powder forming cake or puff in vial bottom. Clumping, discoloration, visible moisture suggest degradation or poor lyophilization. However, appearance alone cannot confirm purity or identity, many contaminants invisible.
Reconstitution behavior: Properly lyophilized peptide should dissolve readily in bacteriostatic water within minutes with gentle swirling. Failure to dissolve or visible particles after reconstitution raise concerns. However, dissolution ease affected by many factors not just purity.
Limitations: Visual and reconstitution assessments provide minor supplemental information. Cannot replace analytical testing. Some underdosed or contaminated products appear perfectly normal. Never rely solely on visual inspection for quality determination.
Proper storage preventing degradation
Lyophilized storage: Unopened vials stored at -20°C (freezer) or 2-8°C (refrigerator) with desiccant maintaining dryness. Freezer storage optimal for long-term (6+ months). Refrigerator acceptable for shorter periods (3-6 months). Room temperature storage acceptable only briefly (1-2 weeks) though degrades faster.
Reconstituted storage: Once mixed with bacteriostatic water, refrigerate at 2-8°C. Use within 7-14 days for optimal potency. Some degradation occurs in solution, longer storage reduces effective dose. Freezing reconstituted peptide potentially damages structure, not recommended.
Temperature monitoring: Avoid temperature cycling (repeatedly removing from fridge/freezer then returning). Each cycle creates condensation and temperature stress degrading peptide. Remove only when ready to use, minimize time at room temperature.
Light protection: Store in original amber vials or wrap in aluminum foil protecting from light. Photodegradation affects some peptides though IGF-Des relatively stable. Light protection good practice regardless.
Proper storage maintaining quality: Even 99% pure pharmaceutical-grade peptide degrades to 70-80% purity with poor storage. Vendor quality meaningless if improper handling destroys product. Understanding peptide storage protects investment.
Recognizing degradation signs
Reduced effectiveness: Same dose producing weaker effects than previously suggests degradation. However, many factors affect response (training status changes, diet, receptor sensitivity), so effectiveness changes not definitive degradation indicator without other evidence.
Physical changes: Discoloration (yellowing, darkening), visible particles in reconstituted solution, unusual odor, failure to reconstitute suggest degradation. However, absence of physical changes doesn't guarantee potency, some degradation invisible.
Post-injection reactions: Increased pain, swelling, redness at injection sites might indicate bacterial contamination from degraded bacteriostatic water or contaminated peptide. However, injection reactions also possible from proper peptide if technique poor or individual sensitivity.
When unsure: If suspecting degradation but uncertain, send sample for testing comparing to results from fresh batch. Purity testing reveals whether degradation occurred. Alternatively, obtain fresh vial from reliable source, if effects clearly superior, confirms previous batch degraded.
Safety considerations for research use
Quality verification only one aspect of safe peptide research.
Health monitoring protocols
Baseline assessment: Before starting IGF-Des research, establish health baseline through blood work (glucose, HbA1c, IGF-1 levels, insulin, lipid panel, liver enzymes), blood pressure measurement, body composition assessment. Provides reference for monitoring changes.
Ongoing monitoring: Retest every 8-12 weeks during active use. Watch for hypoglycemia signs (IGF-Des affects glucose metabolism), unusual fatigue or weakness, joint pain (IGF affects connective tissue), unusual growth patterns. Regular monitoring catches problems early.
Glucose management: IGF-Des lowers blood glucose by increasing insulin sensitivity. Some users experience hypoglycemic episodes especially on empty stomach. Keep fast-acting carbohydrates available. Monitor symptoms (shakiness, sweating, confusion, rapid heartbeat). Adjust dosing or timing if hypoglycemia occurs.
Medical supervision: Working with physician understanding research peptide use ideal though many physicians unwilling or unfamiliar. At minimum, regular check-ups monitoring general health. Disclose peptide use if seeking medical care for any reason (relevant for treatment decisions, medication interactions).
Contamination risks and prevention
Bacterial endotoxins: Poor-quality synthesis or non-sterile handling introduces bacterial contamination. Symptoms include fever, flu-like illness, injection site infections. Prevention through verified vendors, proper sterile technique for reconstitution and injection, never reusing needles or vials.
Heavy metal contamination: Synthesis residues might include lead, cadmium, mercury from reagents or equipment. Low-level chronic exposure accumulates. Symptoms subtle (fatigue, cognitive issues) and develop slowly. Prevention through vendor verification and testing showing heavy metals below detection limits.
Incorrect peptide substitution: Unscrupulous vendors substituting cheaper peptides (standard IGF-1, unrelated growth factors, completely different compounds) hoping customers won't test. Taking wrong peptide produces unexpected effects, potential health consequences. Prevention through mass spectrometry confirmation of molecular weight.
Dosing uncertainty from underdosing: Product labeled 5mg containing only 2mg creates accidental overdosing when user assumes label accurate and doses accordingly. Always base protocols on tested purity adjusting for actual peptide content.
Legal and ethical considerations
Research vs human use: Technically all IGF-Des should be "research purposes only not for human consumption." However, clearly many users consume for performance enhancement. This creates legal ambiguity and ethical tension. Self-experimentation carries both legal risks (minimal but present) and health risks (unknown long-term effects).
Anti-doping violations: Athletes subject to WADA testing must avoid all IGF variants (Des, LR3, standard) as prohibited substances. Detection in testing creates serious consequences (suspensions, bans, loss of achievements). Recreational athletes not subject to testing face no anti-doping concerns though ethics of performance enhancement remain personal decisions.
Medical necessity vs performance enhancement: Using IGF-Des for legitimate medical deficiency under physician supervision very different ethically from performance enhancement in healthy individuals. However, prescription access essentially nonexistent for IGF-Des, forcing those wanting to use into research chemical market regardless of rationale.
Informed consent: Self-experimentation requires thorough understanding of risks, benefits, alternatives, legal status. SeekPeptides provides educational resources enabling informed decisions though cannot replace medical advice or eliminate research use risks.
Future sourcing landscape
Evolving regulations and market forces changing IGF-Des availability.
Regulatory trends
Increased scrutiny: Government agencies worldwide increasing attention to research chemical markets. Some countries implementing stricter controls, requiring better vendor documentation, limiting online sales. Trend toward more regulation not less over time.
Vendor compliance: Some legitimate research chemical vendors improving quality control and documentation anticipating regulatory changes. Others operating on margins may exit market rather than invest in compliance infrastructure. Market consolidation toward fewer but more professional vendors possible.
Pharmaceutical alternatives: As research expands understanding IGF-1 variants, pharmaceutical companies might develop approved medications. However, development costs high and muscle enhancement indication unlikely to gain approval. Pharmaceutical IGF products probably remain limited to rare disease indications.
Market evolution
Testing services normalization: Independent testing becoming standard expectation. Vendors without verified quality face increasing skepticism. Community testing initiatives expanding creating more verified vendor data.
Price pressures: Competition among vendors could drive prices down over time. However, increased regulation and quality requirements might increase costs. Net effect uncertain, potentially stable pricing with better quality standards.
International sourcing: As domestic regulations tighten in some countries, international sourcing potentially becoming more important. However, customs enforcement also improving creating countervailing pressure. Cross-border peptide commerce increasingly complex.
SeekPeptides monitors regulatory developments keeping community informed about sourcing landscape changes.
How SeekPeptides supports IGF-Des sourcing
SeekPeptides provides comprehensive resources for safe, effective peptide sourcing.
Detailed vendor reviews aggregating community testing results and experiences. Updated regularly reflecting vendor quality changes over time.
Testing guides explaining analytical methods, interpreting results, selecting laboratories. Empowering independent quality verification.
Protocol resources for research applications. Dosing strategies, timing optimization, cycle planning. Evidence-based approaches maximizing benefits while minimizing risks.
Safety information covering health monitoring, recognizing adverse effects, proper injection technique. Supporting responsible research practices.
Community forums connecting researchers for vendor recommendations, testing collaboration, protocol discussion. Collective knowledge exceeding any individual experience.
Legal resources explaining jurisdiction-specific regulations, importation laws, enforcement patterns. Informed decision-making about legal considerations.
SeekPeptides remains committed to transparent, evidence-based peptide information supporting safe and effective research.
Helpful resources
In case I don't see you, good afternoon, good evening, and good night. May your sources stay reliable, your peptides stay pure, and your research stay safe. Join SeekPeptides.